How Much House Can I Buy on $80K Per Year? A Guide to Home Affordability

1. Understanding the 28/36 Rule and Affordability Basics
One of the first steps in determining how much house you can afford is applying the 28/36 rule. Financial experts recommend that your housing expenses (mortgage, taxes, and insurance) should not exceed 28% of your gross monthly income. On an $80,000 annual salary, this translates to about $1,867 per month for housing costs. Additionally, your total debt—including car loans, student loans, and credit card payments—should not exceed 36% of your income, or approximately $2,400 per month.

2. Calculating Your Maximum Home Price
The amount of house you can buy isn’t determined by your salary alone. Lenders consider factors like your down payment, credit score, loan term, and interest rates. Assuming a 30-year fixed mortgage at a 6% interest rate, a 20% down payment, and no significant debt, you may qualify for a home priced between $250,000 and $350,000. A lower down payment or higher debt levels could reduce this range.
Online mortgage calculators are excellent tools to estimate your buying power. Simply input your income, down payment amount, and estimated interest rate to find a realistic home price. Remember to account for additional costs such as private mortgage insurance (PMI) if your down payment is less than 20%.

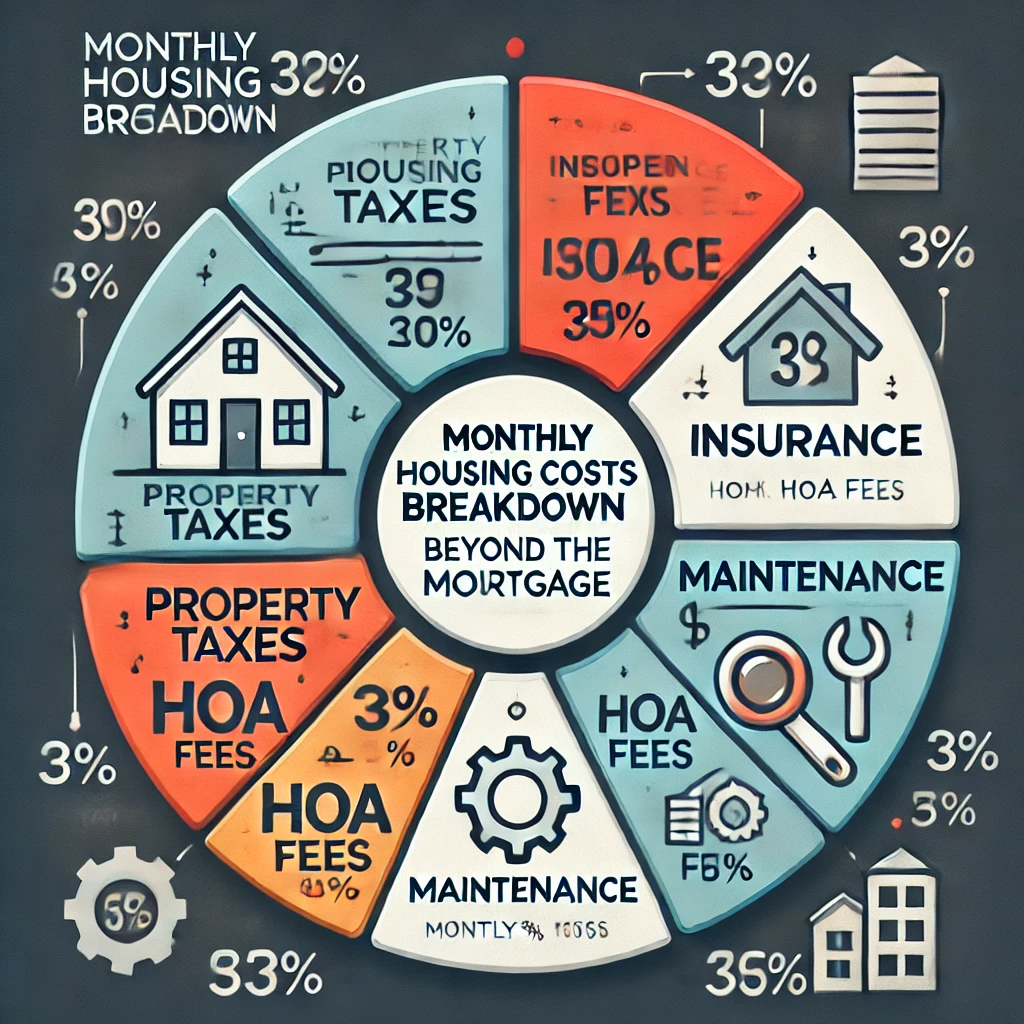
3. Factoring in Property Taxes, HOA Fees, and Other Expenses
Owning a home involves more than just paying the mortgage. Property taxes, homeowners’ insurance, and potential HOA (Homeowners’ Association) fees can significantly impact your monthly housing costs. For instance, property taxes vary widely by state and county, ranging from 0.3% to over 2% of your home’s value. On a $300,000 house, this could mean $900 to $6,000 annually.
When budgeting, also consider maintenance and repair costs, which typically average 1% of the home’s value per year. These expenses ensure your home retains its value and avoids costly surprises.
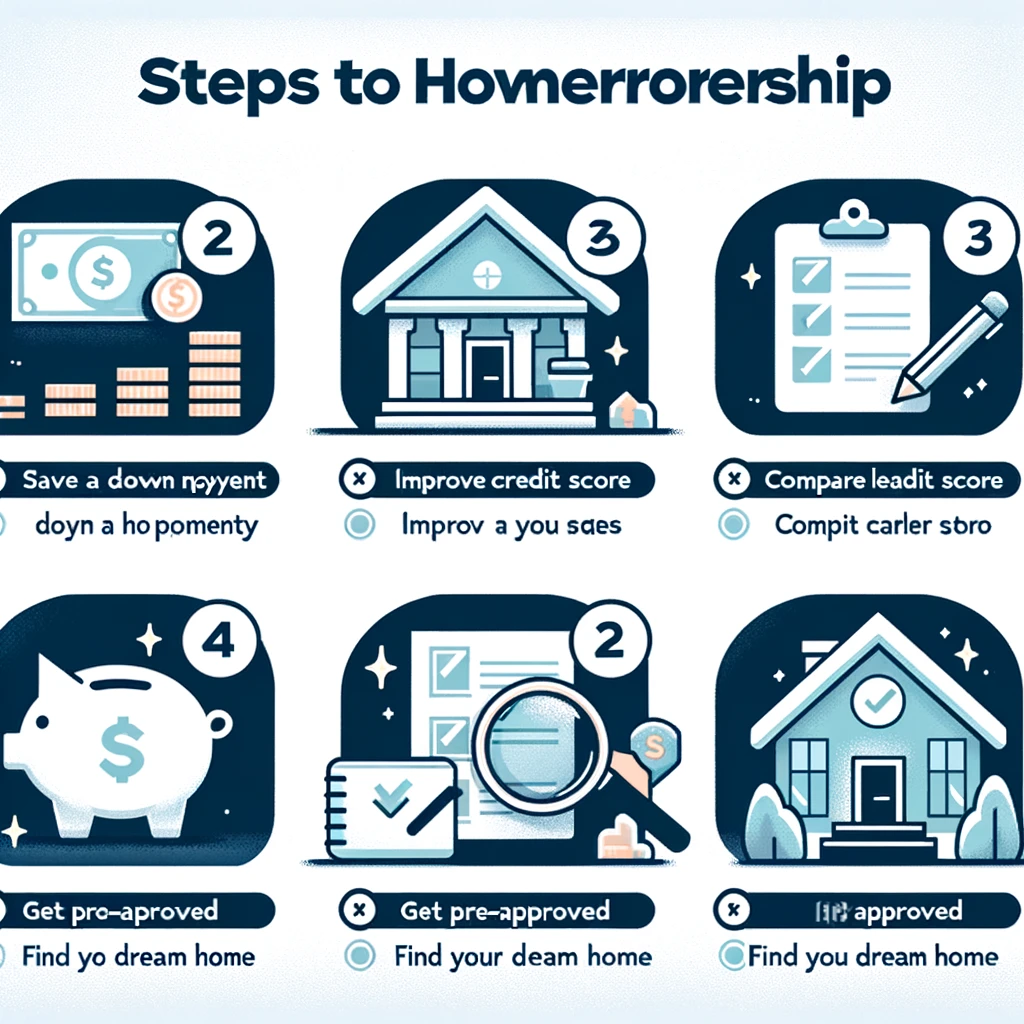
4. Strategies to Maximize Your Home-Buying Budget
To stretch your budget, consider the following tips:
- Increase Your Down Payment: Saving for a larger down payment reduces your loan amount and monthly payments.
- Improve Your Credit Score: A higher credit score can help you secure lower interest rates, saving thousands over the life of the loan.
- Shop Around for Lenders: Different lenders offer varying loan terms and interest rates, so compare offers to find the best deal.
- Reduce Debt: Paying off high-interest debts before applying for a mortgage increases your buying power.
These strategies can make a significant difference in your affordability range, allowing you to buy a home that meets your needs without financial strain.
5. Planning for Long-Term Affordability
Buying a home is a long-term commitment, and it’s essential to plan for the future. Before committing to a mortgage, ask yourself:
- Will your income likely increase over time?
- Are you prepared for potential job changes or economic downturns?
- Have you saved an emergency fund to cover 3-6 months of expenses?
Being realistic about these questions ensures you won’t overextend yourself financially. Aim to leave room in your budget for savings, investments, and unexpected expenses. Homeownership is about stability, not stress.

Conclusion
Earning $80,000 per year provides a solid foundation for homeownership, but the key to success is understanding your financial limits and planning wisely. By following the 28/36 rule, using mortgage calculators, and accounting for all housing-related costs, you can confidently navigate the home-buying process. With careful budgeting and a clear understanding of your priorities, your dream home can become a reality without compromising your financial future.
Categories
Recent Posts






"My job is to find and attract mastery-based agents to the office, protect the culture, and make sure everyone is happy! "
